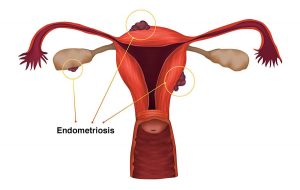
Endometriosis is a benign, recurrent, gynecological disease in which tissue, similar to the endometrium, the mucous layer in the uterine cavity, grows outside the uterine cavity. Benign means that the cells do not degenerate into an oncological process. Recurrent, because both with drug and surgical treatment, there is a fairly high probability of the appearance of new foci. Endometriosis is one of the possible causes of chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS)
Despite the fact that more than 150 years have passed since the appearance of data on this disease, the exact reasons for its appearance are still unknown. It is impossible to completely cure endometriosis, almost all experts agree with this. Numerous current clinical studies support this information. But you can stop its development, reduce manifestations, reduce the risk of spread.
The prevalence of the disease is growing, every 10 women, according to statistics, suffer from this pathology. There are several explanations for the upward trend in morbidity. First, diagnostics are becoming more accurate and more accessible, which increases detectability. This is also due to the fact that women began to give birth less and later, respectively, there are much more menstruation and they come longer than the body expected and as nature intended.
Reasons for the appearance
The most likely cause of endometriosis is considered to be retrograde menstruation, when endometrial particles with blood enter the abdominal cavity through the fallopian tubes. Endometrioid cells are distinguished by their viability, they can maintain activity and start the mechanism of vascular germination in the area where they are. It turns out that they are able to independently produce the female sex hormone estradiol from male hormones that penetrate through the blood vessels. A large amount of estrogen activates the growth of the focus, thus, the cells in the focus of endometriosis stimulate themselves to grow.
But not all endometrial cells differ in their ability to penetrate into tissues. Retrograde menstruation occurs in almost 90% of women, and on average, about 10% encounter endometriosis (according to various sources, from 2 to 15%). It can be concluded that additional conditions are needed for the development of endometriosis, and that cells that have entered the abdominal cavity in healthy women do not attach or grow.
What increases the risk of cell attachment and endometriosis?
It turned out that there are many such factors. The most significant are:
inflammation, which creates the most favorable soil for the attachment of endometrial cells;
prolonged, heavy menstrual bleeding, in which there is a higher risk of blood flowing where it should not be;
narrowing of the lumen of the cervical canal, for example, after surgery, abortion.
Additional risk factors include reduced immunity, low physical activity.
Endometriosis manifestations
Most often, with the defeat of the female genital organs, patients are worried about pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region. This pain can be cyclical, associated with menstruation. Spotting discharge from the genital tract before and after menstruation. Pain during intercourse. Endometriosis causes infertility and miscarriage.
With damage to the intestines, bladder, signs of a violation of their function appear: blood in the feces, constipation, urinary disorders, blood in the urine. Many women develop neurological disorders: radiculoneuritis, pain in the coccyx, irritability, fatigue, headache, asthenia, depression.
Of great importance is the cyclical nature of the manifestations of the disease and the connection between exacerbation and menstruation.
If the patient is observed for a long time with symptoms of irritable bowel or cystalgia and does not receive the effect of traditional therapy, it is necessary to exclude endometriosis of the intestine or bladder.
Survey
There are two questions for women, positive answers to which require a visit to a gynecologist and a diagnostic examination: “Does cyclical pain in the lower abdomen associated with menstruation bother you?” and “Have there been any unsuccessful attempts to get pregnant?”
The possibilities of modern diagnostics to detect this disease are wide enough. Doctors can use ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs and abdominal cavity, computed and magnetic resonance imaging, hysteroscopy, and laparoscopy.
Screening methods at the first stage are a gynecologist’s examination, pelvic ultrasound, colposcopy. Presumptive ultrasound diagnosis during subsequent operative examination is confirmed in 91% of women. But screening methods are non-specific and only allow suspecting a diagnosis, albeit with a high degree of probability.
For a more accurate diagnosis, a laparoscopic study with targeted biopsy of suspicious lesions is necessary, which remains the “gold standard” in the diagnosis of genital endometriosis. The degree of organ damage often does not correspond to the severity of the manifestations of the disease, which is why only examination directly during the operation can determine the stage of the disease.
Treatment
Endometriosis actively affects women of reproductive age, for whom it is extremely important to maintain the ability to conceive and carry a child. It is also important to ensure a good quality of life for all patients, therefore, according to the general opinion of leading gynecologists, when developing standards, a new strategy is currently being applied – therapy, if possible, should be medication.
That is, when a diagnosis is made or a given disease is suspected, we begin treatment with the use of medications, and only in the absence of a positive effect within 6 months, the issue of surgical intervention is decided.
Even if after six months the need for surgical treatment remains, it is not worth stopping therapy, since without it every second woman will be reoperated due to a relapse of the disease.
For therapy, first-line drugs are recommended: combined hormonal contraceptives; progestins (derivatives of progesterone); non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics for pain relief.
The doctor determines the choice of the drug, the regimen and duration of therapy depending on the clinical variant of endometriosis. The tactics are influenced by the severity of symptoms and the stage according to laparoscopy, and, in many respects, the age of the woman and the period before the planned pregnancy.
The main requirement for drug therapy is duration, and this is confirmed by numerous studies.
Indications for surgical treatment of endometriosis: endometrioid ovarian cysts, purulent inflammation of the uterine appendages affected by endometriosis, adhesions, involvement of organs and body systems in the pathological process with impaired functions, lack of a pronounced effect from drug therapy, carried out continuously for 6 months.
It is extremely important to remember that surgical treatment of endometriosis https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endometriosis does not provide complete elimination of the disease. There are always surviving cells that can stay in the abdominal cavity for a long time without causing any symptoms. As they progress, they are capable of causing relapses of the disease. That is why, in order to stop the development of endometriosis, medications are prescribed for a long time at the stage of treatment after surgery.